Streptococcus Pyogenes
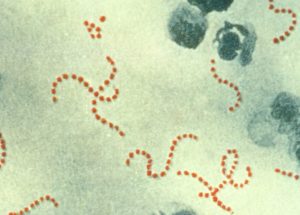 Streptococcus pyogenes is a species of Gram-positive bacteria. These bacteria are aerotolerant and are made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci. Therefore they are clinically important in human illness.
Streptococcus pyogenes is a species of Gram-positive bacteria. These bacteria are aerotolerant and are made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci. Therefore they are clinically important in human illness.
Epidemiology:
- Throat
- Genital mucosa
- Rectum
- Skin
1% to 5% of healthy individuals have the throat, vaginal, or rectal carriage because it is the site of their colonization.
While in healthy children, such carriage rate varies from 2% to 17%.
Methods of Transmission of Streptococcus Pyogenes:
- Inhalation of respiratory droplets
- Skin contact
- Contact with objects
- Surface
- Dust that is contaminated with bacteria
- Commonly transmission through food
Bacteriology:
They cause diseases such as
- Streptococcal pharyngitis,
- Rheumatic fever,
- Rheumatic heart disease
- Scarlet fever
S. pyogenes infection is more frequently found in men than women. It usually happens within one week of the diagnosis of influenza infection.
S. pyogenes serotyping:
S. pyogenes isolates based on their surface T-antigen. Four of the 20 T-antigens have been revealed to be pili.
Virulence factors:
- S. pyogenes has several virulence factors:
- Bacterial capsule composed of hyaluronic acid
- M protein
- Lipoteichoic acid
- Protein F
Lysogeny:
They are all polylysogenized, in that they carry one or more bacteriophage on their genomes.
- Streptolysin O
- Streptolysin S
- Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A (SpeA)
- Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin C (SpeC)
- Streptokinase
- Hyaluronidase
- Streptodornase
- C5a peptidase
- Streptococcal chemokine protease
Watch World’s Best Lecture on S. pyogenes – FREE ACCESS FOR 7-DAYS
Disclaimer: The information provided on this website (www.MadeForMedical.com) is only for educational purpose. While we try hard to write quality articles but still, the articles and the information within them is not guaranteed to be free of factual errors or typos and hence may not be correct. You are advised to independently verify the claims in the articles and make your own conclusion.
