Streptococcus Agalactiae
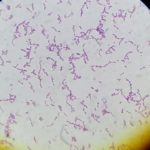 Streptococcus agalactiae is a gram +ve cocci and causes beta-hemolysis of RBCs in the blood agar. It is a catalase -ve bacterium and therefore it does not respond to the catalase test. It has a polysaccharide capsule because of what, it is of more pathogenic nature.
Streptococcus agalactiae is a gram +ve cocci and causes beta-hemolysis of RBCs in the blood agar. It is a catalase -ve bacterium and therefore it does not respond to the catalase test. It has a polysaccharide capsule because of what, it is of more pathogenic nature.
Colonization
As this bacteria is pathogenic to humans, therefore it can colonize at the following sites in the human body
- Intestines
- Vagina
- Urinary tract
WATCH WORLD’S BEST VIDEO LECTURE ON THIS TOPIC (SIGNUP REQUIRED)
Virulence Factors of Streptococcus Agalactiae
Virulence factors are the factors, which a microorganism possess to causes disease in the host. These organisms have the following virulence factors
- A polysaccharide capsule
- Beta-hemolysin toxin
Laboratory Diagnosis
- It causes beta-hemolysis of RBCs in the blood agar, because of this, they can be identified.
- They are CAMP-test +ve
Infections Because of S. Agalactiae
As this organism is pathogenic in nature, therefore it causes the following infections:
- Urinary tract infection
- Neo-natal septicemia
- Meningitis
- Sepsis
Treatment
Penicillin or Ampicillin have been proven to be effective against Strep Agalactiae. Because these organisms are not resistant to penicillin majority of the times. Therefore penicillin or ampicillin are used against these bacteria.
WATCH WORLD’S BEST VIDEO LECTURE ON THIS TOPIC (SIGNUP REQUIRED)
Medical Disclaimer:
The information provided on this website (www.MadeForMedical.com) is only for educational purpose.
While we tried hard to write quality articles but still, the articles and the information within them is not guaranteed to be free of factual errors or typos and hence may not be correct. You are advised to independently verify the claims in the articles and make your own conclusion.
